Is this an alien skeleton? Bizarre egg-shaped skull unearthed from 4,000 years ago

Is this an alien skeleton? Bizarre egg-shaped skull unearthed from 4,000 years ago
A skeleton found at a site known as Stonehenge in Russia has sparked fresh ideas about the extraterrestrial visitor to earth. When images of the remains were first published, UFO enthusiasts rushed to claim they were proof that aliens had once visited Earth.
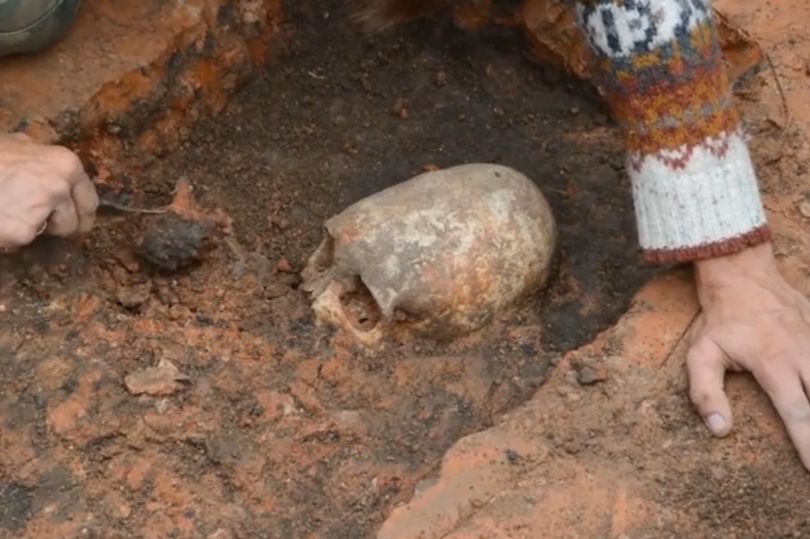

But archaeologists revealed that the bones belong to a woman who had an elongated skull because it was bound out of tribal tradition, who lived almost 2,000 years ago
The remains of this settlement date back almost 4,000 years and were found in Arkaim, near Chelyabinsk in Central Russia. It is assumed that the woman belonged to a tribe that was part of what is now modern day Ukraine.
Researcher Maria Makurova has confirmed to the Russian news agency TASS: ‘We have found a well-preserved skeleton.
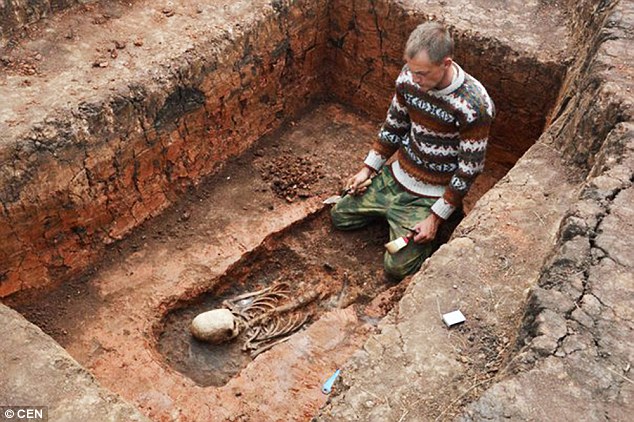

‘I would not exclude the possibility that the skeleton belongs to a woman from the Sarmati tribe that lived in the territories of what is now modern day Ukraine, Kazakhstan and southern Russia.
‘Her skull was elongated because the tribe did so by tying up the heads of their children with rope. It was clearly a tradition in the tribe.’

She declined to comment on speculation it was attributed to alien visitors saying that currently they were still working on theories as to why the tribe had the tradition but had nothing fixed yet as a reason.
The skeleton is thought to date to the second or third century AD, making it considerably younger than the site.
It is just another of the mysteries to be unearthed at the spectacular site of Arkaim known as Russia’s Stonehenge, which is believed to have been built in the 17th century BC.
It is believed by some that, like its 5,000-year-old English counterpart, it was used to study of the stars.
But Arkaim is thought to be more advanced.
Stonehenge allows for observations of 10 astronomical phenomena using 22 elements, while Arkaim enables observations of 18 phenomena using 30 elements.
This means that ancient people could have observed and tracked certain events in the sky by using the site in certain ways from particular positions, and that Arkaim offered more observable events than Stonehenge.
Russian archaeologist K.K. Bystrushkin, who made the comparison between the two sites in 2003, said Stonehenge offers an observational accuracy of 10-arc minutes to a degree, whereas Arkaim offers accuracy of one-arc minute.
This precision was unheard of at the time the monument is thought to have been built.

The Akraim archaeological site was discovered in 1987 and since then it has yielded spectacular discoveries including some artefacts from the Bronze Age.
As well as being a primitive astronomical observatory it was also a village that was fortified by two large stone circular walls.
The settlement covers an area of some 220,000 square feet (20,439 square metres) and consists of two circles of dwellings separated by a street, with a central community square in the centre.