Wooden Shigir idol found to be over twice as old as Egyptian pyramids

Wooden Shigir idol found to be over twice as old as Egyptian pyramids
A twice as old as the Egyptian pyramids, scientists have found a giant, human-like figure, cut out from wood and discovered in Russia.
In 1894, gold miners discovered the elongated structure called the Shigir Idol.
However, in the late 1990s, about 100 years later, researchers found that it was about 9,900 years old and the structure became the oldest monumental wooden sculptures worldwide, the scientists said.

But this dating wasn’t reliable because it included only two pieces from the idol. So scientists recently did a more exhaustive analysis and discovered that the idol is much, much older than previously thought — about 11,500 years old — meaning it was constructed just after the last ice age ended.
This date makes the Shigir Idol more than double the age of the Great Pyramid of Egypt, which was built in about 2550 B.C.
In addition to updating the sculpture’s birthday, the researchers found a previously unknown face carved into it, said study co-researcher Thomas Terberger, an archaeologist at the State Agency for Heritage Service of Lower Saxony, in Hannover, Germany.

Incredible find
It’s a “miracle” that the Shigir Idol survived all this time, Terberger told Live Science.
Researchers began studying the larch-carved figure after it was found in the Shigir peat bog, in Russia’s Middle Ural Mountains. Pieced together, the sections of the humanoid idol stood more than 17 feet (5 meters) high.
Unfortunately, some of those sections have since been lost, so the idol now stands about 11.1 feet (3.4 m) high, Terberger said. The public can see the carved anthropomorphic figure at the Sverdlovsk Regional Museum.
“When I visited the Sverdlovsk Regional Museum for the first time, I was completely surprised by seeing this large wooden sculpture on display in the exhibition,” Terberger said. “If you come closer to the sculpture, you will notice that the ‘body’ is decorated by geometric ornamentation and a few small human faces.”
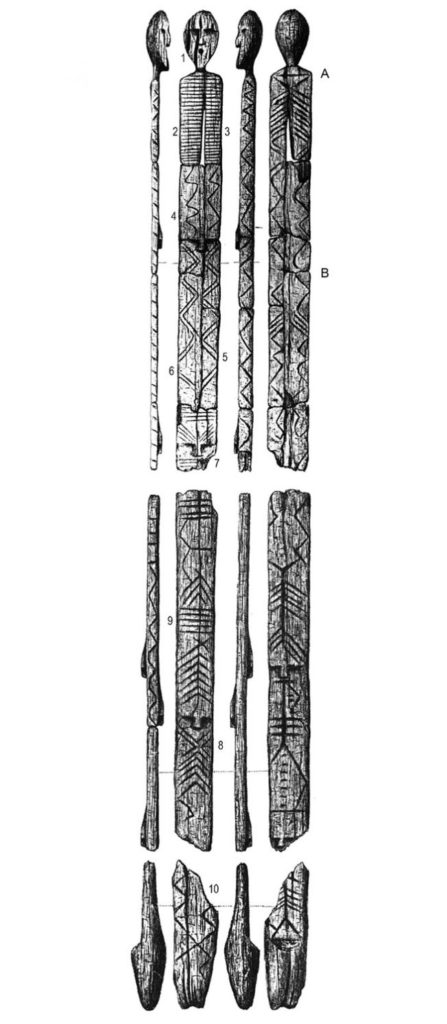
Some 20 years after it was discovered, researcher Vladimir Yakovlevich Tolmachev drew illustrations of the idol, noting the structure’s five faces, the researchers of the new study noted.
In 2003, a sixth, animal-like face with a rectangular nose was found by study co-researcher Svetlana Savchenko, a scientist at the Sverdlovsk Regional Museum.
Just like a hidden-pictures game, the idol surprised researchers again in 2014, when Savchenko and lead study researcher Mikhail Zhilin, an archaeologist at the Institute of Archaeology in Moscow, discovered a seventh face concealed in the gnarled wood.
These facial findings show that the early hunters, gatherers, and fishers of Eurasia were making what was possibly spiritual art during the early Mesolithic, the researchers said.
“Such a big sculpture was well visible for the hunter-gatherer community and might have been important to demonstrate their ancestry,” Terberger said. “It is also possible that it was connected to specific myths and gods, but this is difficult to prove.”
Terberger noted that many researchers studying early humans focus on the Fertile Crescent in the Middle East. But the Shigir Idol indicates that these researchers should widen their search, given the “unexpected, complex monumental wooden art objects” of the Ural Mountains, he said.
The study was published online today (April 25) in the journal Antiquity. The research was made possible by Natalia Vetrova, the director of the Sverdlovsk Regional Museum, Terberger added.